Codecs are a crucial part of modern multimedia technology, enabling the compression and decompression of audio and video files. While codecs are behind many of the files and media we use every day, they often remain a mystery to most users. This article aims to demystify codecs and explore the four easy ways to understand and manage them effectively.
1. What Are Codecs and Why Are They Important?
A codec (short for coder-decoder or compressor-decompressor) is software or hardware that compresses and decompresses digital media files. Without codecs, it would be nearly impossible to store, transmit, and play back high-quality video or audio efficiently. Codecs reduce the file size of media while preserving the quality as much as possible. This compression is especially crucial for streaming media, video conferencing, and online content consumption.
There are two main types of codecs:
- Lossy codecs: These remove some of the audio or video information to reduce file size (e.g., MP3, AAC, H.264). The quality loss is usually not noticeable to most users.
- Lossless codecs: These preserve the full quality of the original media file but result in larger file sizes (e.g., FLAC, ALAC, H.265).
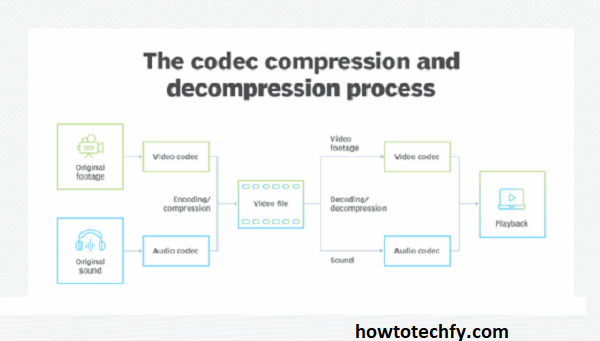
2. Understanding the Most Common Codecs
To better navigate the world of codecs, it’s helpful to know the most common ones you’ll encounter. Here are a few widely-used codecs and their functions:
- MP3 (Audio): One of the most well-known lossy audio codecs, MP3 offers a balance between file size and sound quality. It’s the standard format for music and podcasts.
- AAC (Audio): Advanced Audio Codec (AAC) provides better sound quality than MP3 at similar bit rates and is commonly used in streaming platforms like YouTube and Apple Music.
- H.264 (Video): This lossy video codec is widely used for compressing video files without significant loss of quality. It is the go-to codec for most video content, including Blu-ray discs and online streaming.
- H.265 (Video): Also known as HEVC (High-Efficiency Video Coding), H.265 offers better compression and video quality than H.264, making it ideal for 4K streaming and high-resolution videos.
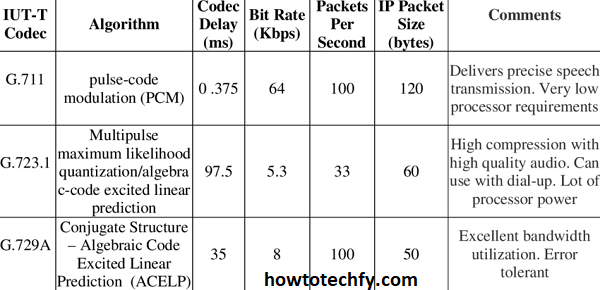
Understanding which codecs are needed for specific devices or software can help you avoid compatibility issues and enhance your viewing or listening experience.
3. How to Manage Codecs on Your Device
Codecs are often embedded into media players and devices, but sometimes you may need to install additional codec packs to play certain media files. Here are four easy ways to manage and handle codecs:
- Install Codec Packs: If your media player can’t play a specific file format, try installing a codec pack. Programs like K-Lite Codec Pack offer a comprehensive set of codecs for playing most audio and video formats on Windows.
- Use Universal Media Players: Some media players, such as VLC Media Player, come with built-in support for a wide range of codecs. This allows you to play virtually any media file without worrying about installing separate codecs.
- Update Your Software: Ensure your media players and devices are regularly updated. New versions often come with updated codec libraries, improving compatibility with the latest media formats.
- Convert Media Files: If you encounter a file with an incompatible codec, consider using a file conversion tool. Software like HandBrake or Freemake Video Converter can convert files into more widely supported formats.
4. How to Stay Secure While Using Codecs
While codecs are essential for media playback, it’s important to be cautious, as some codec-related software can pose security risks. Here’s how to stay secure while using codecs:
- Download from trusted sources: Only download codec packs or media players from reputable websites to avoid malicious software.
- Use antivirus software: Make sure your antivirus is up-to-date to protect against any potential threats associated with codec-related downloads.
- Stay informed about vulnerabilities: Occasionally, vulnerabilities are discovered in certain codecs or media players. Keep an eye on security updates and patch any issues promptly.
FAQs: Unlocking the Mystery of Codecs
1. What exactly is a codec?
A codec (short for coder-decoder or compressor-decompressor) is a tool used to compress and decompress digital media files, such as audio and video. It reduces the file size for easier storage or streaming while maintaining quality as much as possible. When you play a media file, the codec decompresses it for playback.
2. What’s the difference between lossy and lossless codecs?
- Lossy codecs remove some data to reduce file size, which can result in a slight reduction in quality that’s often imperceptible to the human eye or ear (e.g., MP3, AAC, H.264).
- Lossless codecs preserve the full quality of the original media but produce larger files (e.g., FLAC, ALAC, H.265).
3. Why do I need codecs?
Codecs are essential because they enable the efficient storage and transmission of media files. Without codecs, videos and audio would be too large to stream or store on most devices. They help compress media so that it can be easily shared online, stored on hard drives, or streamed over the internet.
4. How do I know which codec I need for a specific file?
If a file doesn’t play on your device, you may need to find the appropriate codec. Tools like MediaInfo can help identify the codec used in a media file. From there, you can install the necessary codec or use a media player (like VLC) that supports a wide range of codecs.
5. Can I install codec packs to play unsupported files?
Yes, installing a codec pack can help ensure you have all the necessary codecs to play a wide variety of media files. For example, the K-Lite Codec Pack includes numerous codecs for both audio and video formats. Just be cautious when downloading codec packs, as some sources may include malware.
6. What’s the best media player for handling various codecs?
VLC Media Player is widely regarded as one of the best universal media players. It comes with built-in support for many popular audio and video codecs, eliminating the need to install additional codec packs. It’s free, open-source, and works across various platforms.
7. Are codec-related software and tools safe to download?
Codec-related software can be safe if downloaded from reputable sources. However, some unofficial codec packs or tools may contain malware or unwanted software. Always download from trusted sites or official app stores, and ensure your antivirus software is active and up-to-date.
8. What’s the difference between H.264 and H.265?
- H.264 is a widely-used video codec that offers good compression with reasonable quality. It is commonly used for streaming services and video formats.
- H.265 (or HEVC – High-Efficiency Video Coding) provides better compression and quality at lower bit rates than H.264, making it ideal for 4K video streaming and high-definition content. However, it requires more processing power to decode.
9. Can I convert media files if I encounter a codec issue?
Yes, you can convert media files into more compatible formats if you encounter codec issues. Tools like HandBrake and Freemake Video Converter allow you to convert files from one format to another, ensuring compatibility with your media player or device.
10. How do I stay secure when using codecs?
To stay secure while using codecs:
- Download codecs only from trusted websites.
- Keep your media players and codec packs up-to-date to avoid known vulnerabilities.
- Use antivirus software to detect any malicious files.
- Be cautious about downloading software from unverified sources, especially when dealing with third-party codec packs or emulators.
Conclusion
Codecs may seem complex, but they are a fundamental part of the media we consume daily. By understanding the basics of codecs, managing them effectively, and staying secure, you can improve your media experience without the frustration of compatibility issues. Whether you’re watching a movie, listening to music, or editing video, knowing how codecs work and how to handle them can help you unlock the full potential of your digital media.

