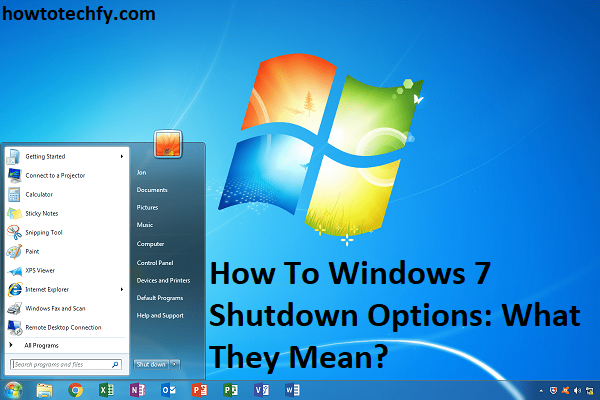
Windows 7 offers several options for shutting down your computer, each designed to suit different needs. Whether you’re stepping away briefly or finishing your workday, understanding these options can help you manage your computer’s power efficiently. Here’s a breakdown of the four main shutdown options in Windows 7 and when to use them.
1. Shut Down (Power Off Completely)
What It Does:
The “Shut Down” option completely powers off your computer. All open programs and processes are closed, and your PC is turned off until you manually power it back on.
When to Use It:
- When you’re done using your computer for the day.
- After installing software or updates that require a restart.
- To conserve energy when you won’t be using the computer for a long period.
How to Access:
- Click the Start button, then click the arrow next to the Shut Down button and select Shut Down.
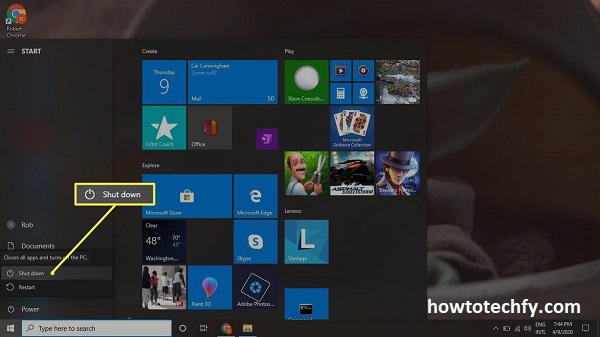
Tip: Save all your work before shutting down to avoid losing unsaved data.
2. Restart
What It Does:
Restart shuts down the computer and automatically reboots it. This option is commonly used after installing updates, software, or drivers that require a fresh start to complete their installation.
When to Use It:
- After software installations or updates.
- When troubleshooting software issues.
- If the computer is running slowly and needs a refresh.
How to Access:
- Click the Start button, then click the arrow next to the Shut Down button and select Restart.
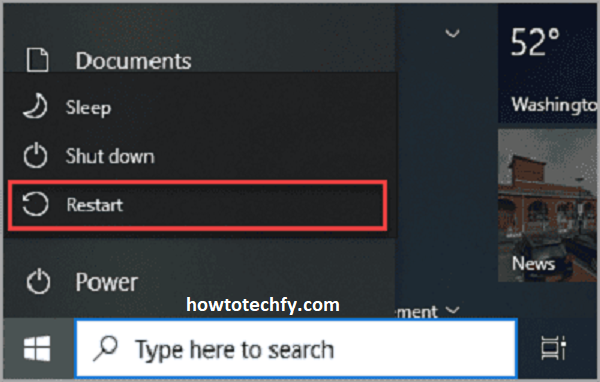
Tip: Restarting can often resolve minor system glitches and performance issues.
3. Sleep
What It Does:
Sleep puts your computer into a low-power state without fully turning it off. All open applications and documents are saved in memory, allowing you to resume your work quickly by pressing a key or moving the mouse.
When to Use It:
- When taking a short break but plan to return soon.
- To save energy while keeping your session open.
- If you want your computer to resume quickly without waiting for a full reboot.
How to Access:
- Click the Start button, then click the arrow next to the Shut Down button and select Sleep.
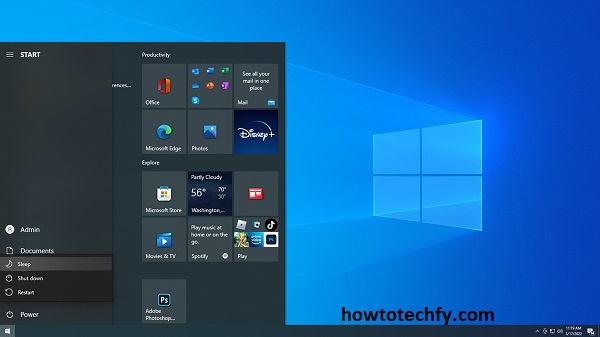
Tip: Sleep is perfect for laptops because it extends battery life while keeping your work accessible.
4. Hibernate
What It Does:
Hibernate saves all open applications and documents to the hard drive and then powers off the computer. When you turn the PC back on, everything is restored exactly as it was. This uses no power while off, unlike Sleep mode.
When to Use It:
- When you want to save your current work session but won’t be using the computer for an extended time.
- If you need to preserve your session during a power outage.
- To conserve battery power while saving your work.
How to Access:
- Click the Start button, then click the arrow next to the Shut Down button and select Hibernate.
Tip: Hibernate is ideal for laptops, especially if you’re traveling and want to save battery.
FAQs: Windows 7 Shutdown Options
1. What is the difference between Shut Down and Restart in Windows 7?
- Shut Down powers off the computer completely, while Restart turns it off and immediately reboots it. Restart is often used after installing updates or troubleshooting issues.
2. When should I use Sleep mode?
- Use Sleep when you plan to return to your computer shortly. It saves your current session and puts the computer in a low-power state, allowing you to resume work quickly.
3. How is Hibernate different from Sleep?
- Hibernate saves your session to the hard drive and powers the computer off, using no electricity. Sleep saves your session in memory and uses a small amount of power to maintain it. Hibernate is ideal for longer periods of inactivity.
4. Can I lose my work if I choose Hibernate or Sleep?
- No, both Hibernate and Sleep save your open applications and files. Hibernate saves to the hard drive, while Sleep keeps them in memory. If your battery dies during Sleep, unsaved work could be lost. Hibernate is safer for long periods.
5. Is it necessary to shut down my computer every day?
- No, Sleep or Hibernate can be used if you plan to use the computer daily. However, shutting down periodically can improve performance and ensure updates are applied.
6. Why does my computer sometimes restart instead of shutting down?
- This can happen if an update is pending or if there is a system issue. Check for Windows updates or troubleshoot for any software conflicts.
7. Can I disable Sleep or Hibernate?
- Yes, you can disable or adjust Sleep and Hibernate settings in Power Options under the Control Panel. This allows you to customize when your computer enters these states.
8. What happens if I press the power button during Sleep or Hibernate?
- Pressing the power button during Sleep or Hibernate will wake the computer. If held down for several seconds, it will force a shutdown, potentially causing data loss.
9. Does Hibernate mode slow down my computer?
- No, Hibernate does not affect performance. It simply saves your session and powers down the system. However, it may take slightly longer to resume compared to Sleep.
10. How can I access Hibernate if I don’t see it in the shutdown options?
- If Hibernate is missing, go to Control Panel > Power Options > Choose what the power buttons do and enable Hibernate under Shutdown settings.
Conclusion
Understanding Windows 7 shutdown options allows you to better manage your computer’s power and performance. Whether shutting down, restarting, sleeping, or hibernating, each option serves a specific purpose. By using these features wisely, you can extend the life of your PC, improve efficiency, and ensure your work is preserved.